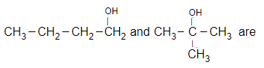Structural Isomerism
Structural Isomerism: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Structural Isomerism, Chain Isomerism, Position Isomerism, Functional Group Isomerism, Ring-chain Isomerism, Metamerism, Tautomerism, Types of Tautomerism, Keto-Enol Tautomerism, etc.
Important Questions on Structural Isomerism
The compound C2H5OC2H5 and CH3OCH2CH2CH3 are
Molecular formula can have (including stereoisomer):
Which two of the following compounds are identical?
Phenol and benzyl alcohol are
How many structural formula are possible when one of the hydrogen is replaced by a chlorine atom in anthracene?
C7H7Cl shows how many benzenoid aromatic isomers?
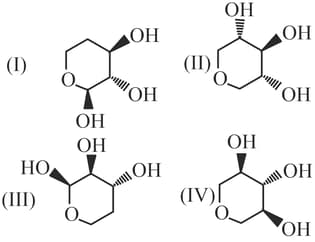
The compounds are:
The enolic form of acetone contains
The total number of structural isomers of C6H14 is:
An isomer of ethanol is:
Which of the following compounds exhibit tautomerism?
Write the structural formulae of all possible isomers of the compound with the molecular formula . Identify the different isomer pairs from them and find the type of isomerism to which each pair belongs.
Write the structural formulae of all possible isomers of .
Ethyl alcohol and dimethyl ether are examples of:
Explain the enolization of acetone in basic solution.
Which of the following are called pseudo acids?
The type of isomerism observed in alkanes is
Which of the following exhibits tautomerism?
Which of the following pairs of compounds are positional isomers?